Formatting & mounting a disk on Windows
Open your Windows VM, right-click the Windows Start button and select Disk Management.
Disk Management is a system utility in Windows that enables you to perform advance storage tasks. Here are some of the things Disk Management is good for:
To set up a new drive
To extend a volume into space that's not already part of the volume on the same drive
To shrink a partition, usually so that you can extend a neighboring partition
To change a drive letter or assign a new drive letter
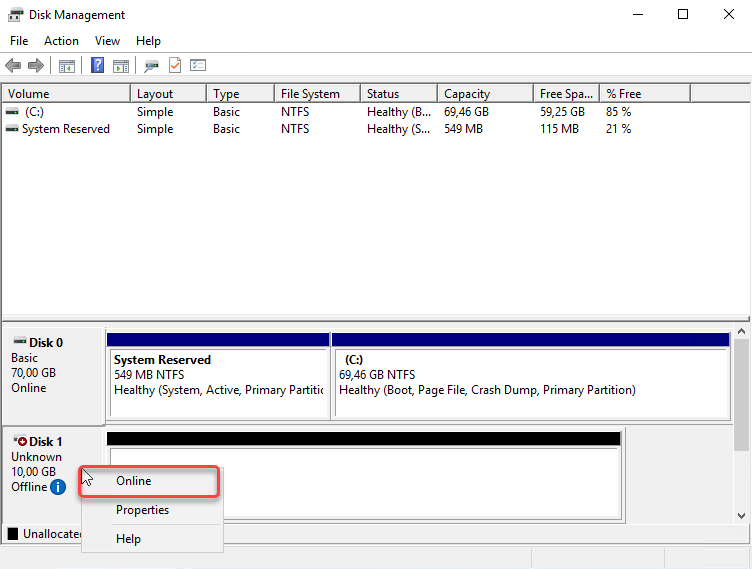
Disk Management will appear, right click on Disk 1, then click Online. You must bring it online before you can initialize it or create volumes on it.
The fields in Disk Management include:
Volume
Partition and logical drives are known as volumes
Layout
The type of the volume
Type
The type of Disk
File System
The types of file system. Disk Management only supports 3 types of file system: FAT,FAT32, and NTFS
Status
The status of volume
Capacity
The capacity of each volume in MB or GB
Free Space
The free space of each volume in MB or GB
% Free
The free space of each volume in %
Disk 0
The single physical drive you have in your system
Disk 1
another single physical drive that you just attached
Disk 0 and Disk 1 are physically different hard disk.
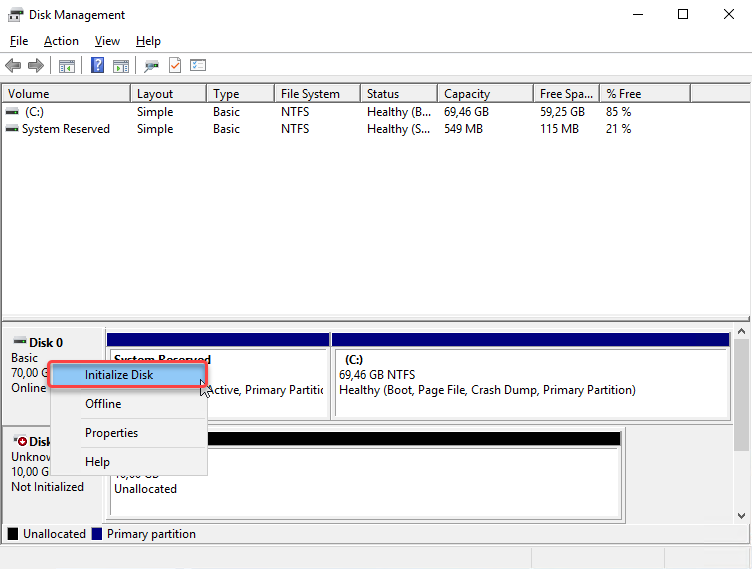
Right click on Disk 1, then click Initialize Disk. Initialize Disk erases everything on it and prepares it for use by Windows, You need initialize it before using it. You can only initialize a drive that's not yet formatted.
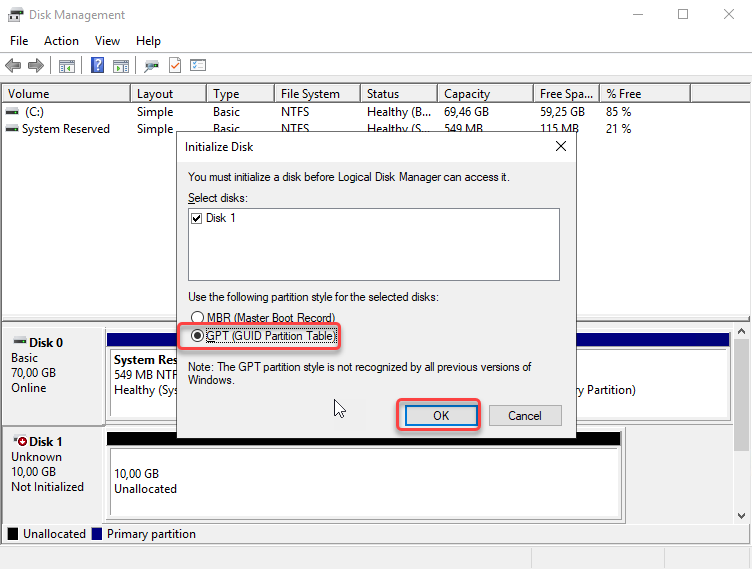
Disk Management prompts you to select a partition scheme for the new disk. Select GPT and click OK.
Disk can be divided up into multiple chunks called partition. Each partition has to have a partition style, GPT or MBR. Windows uses the partition style to understand how to access the data on the disk.
GPT (GUID Partition Table)
The newer GPT partition table style is required on your boot drive by newer computers that use UEFI instead of BIOS. GPT is more robust and allows for volumes bigger than 2TB, and also GPT supports up to 128 partitions on the same hard drive
MBR (Master Boot Record)
Old format partition that is used by 32-bit PCs, older PCs, and removable drives such as memory cards. One of these limitations is that MBR only supports up to 4 primary partitions, the next limitation is that partitions using the MBR format have a maximum size of 2TB
After the disk is initialized, right-click the Unallocated Disk Space and select New Simple Volume.
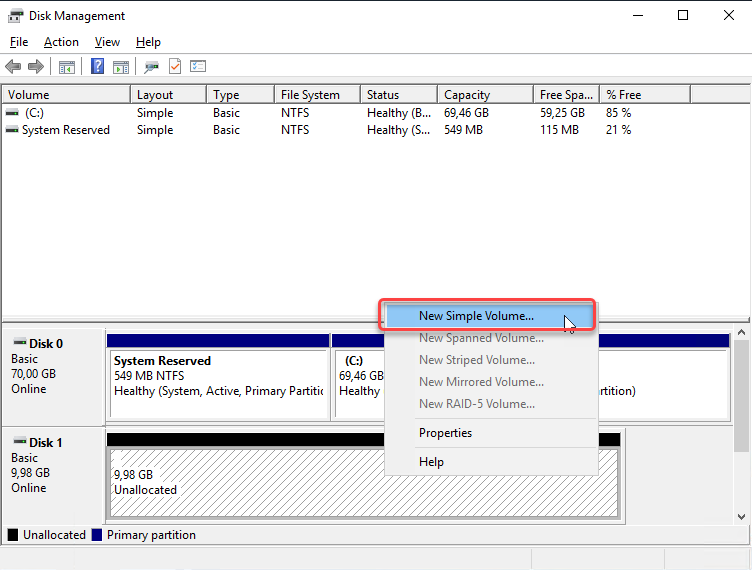
Follow the instructions in the New Simple Volume Wizard to configure a new volume.
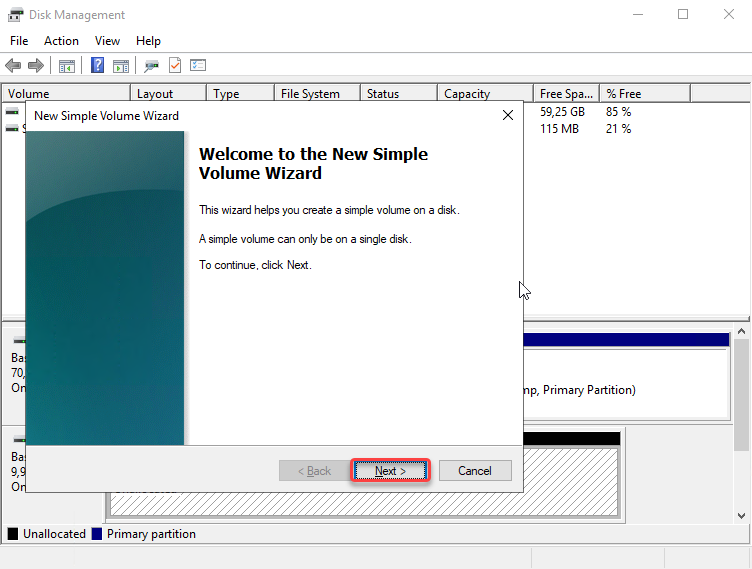
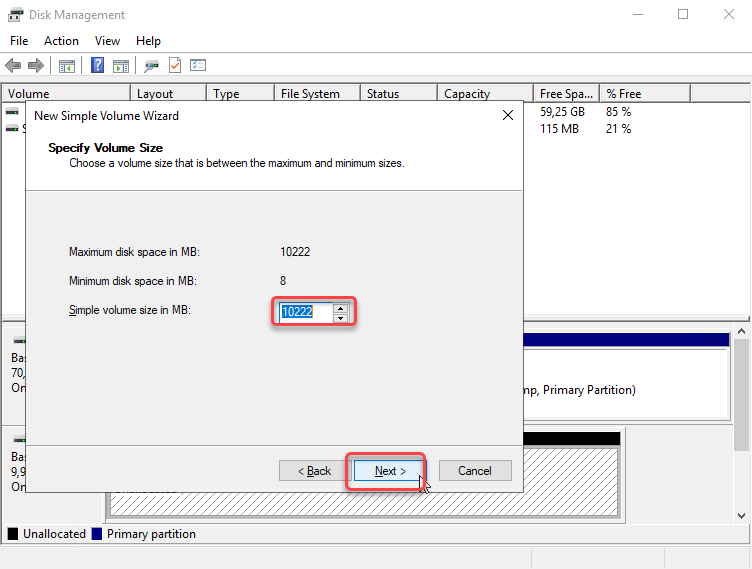
In the Specify Volume Size pop-up, click the Next button.
The field in Specify Volume Size include:
Maximum disk space in MB
The maximum size you can use.
Minimum disk space in MB
The minimum size you can use
Simple volume size in MB
Specify the volume size as needed.
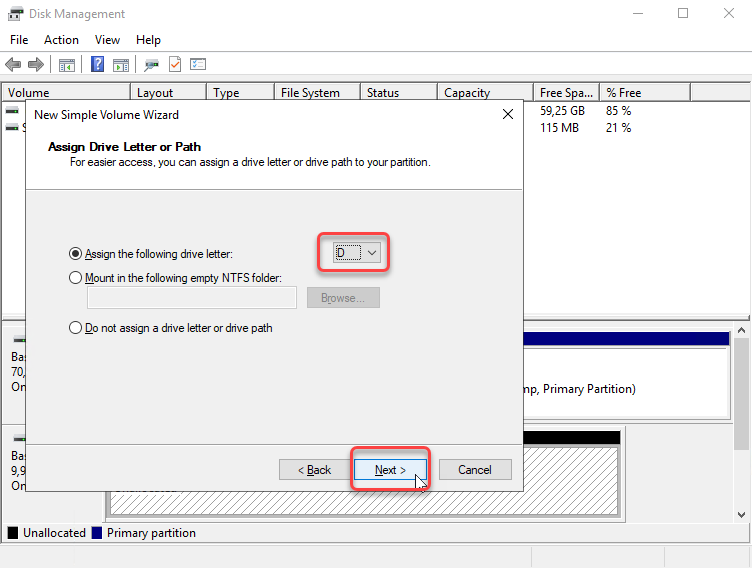
Then on Assign Drive Letter or Path, select Assign the following drive letter, then click Next.
The field in Assign Drive Letter or Path include:
Assign the following drive letter, this option if you want assign the volume to a drive letter.
Mount in the following empty NTFS folder, you can mount (make a drive accessible) in a folder rather than a drive letter if you want. This makes the drive appear as just another folder. You can mount drives only in empty folders on NTFS volumes.
Do not assign a drive letter or drive path, You can choose this option if you don't want to assign a drive letter or drive path.
Next is Format Partition, select Format this volume with the following settings, you can use any partition format you like, but for this example choose NTFS. Also, click the checklist on Perform a quick format to speed up the process. Then click next.
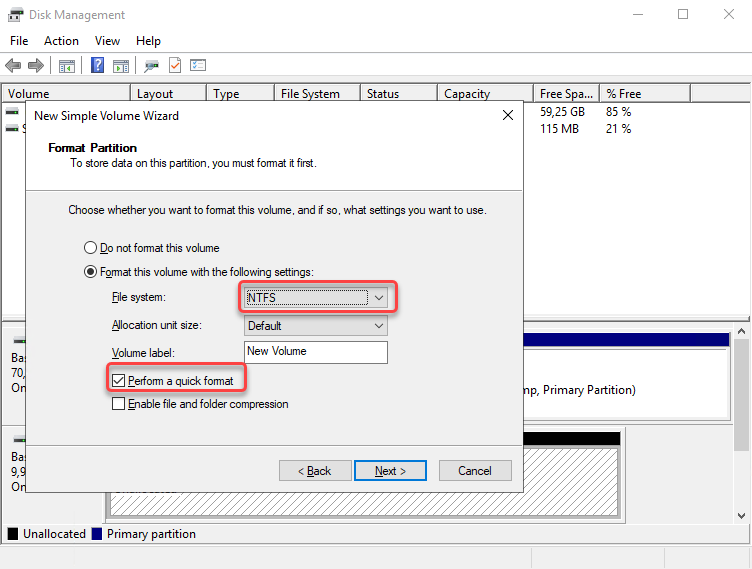
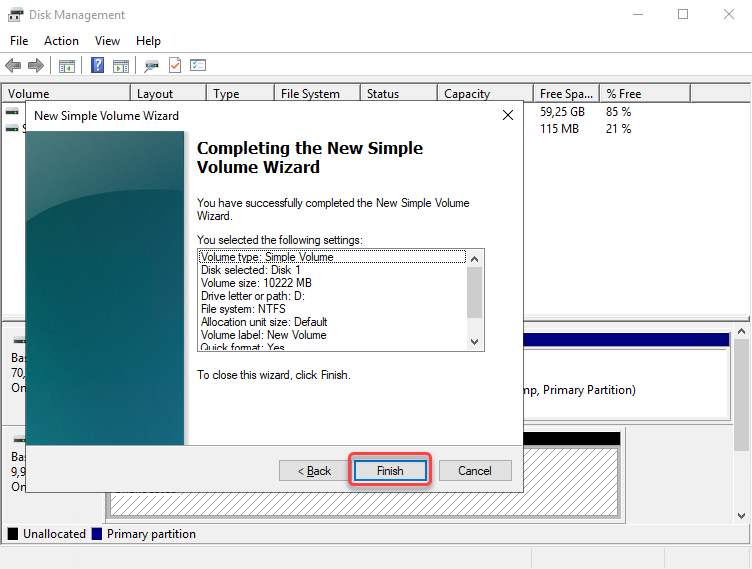
The last step is to click Finish.
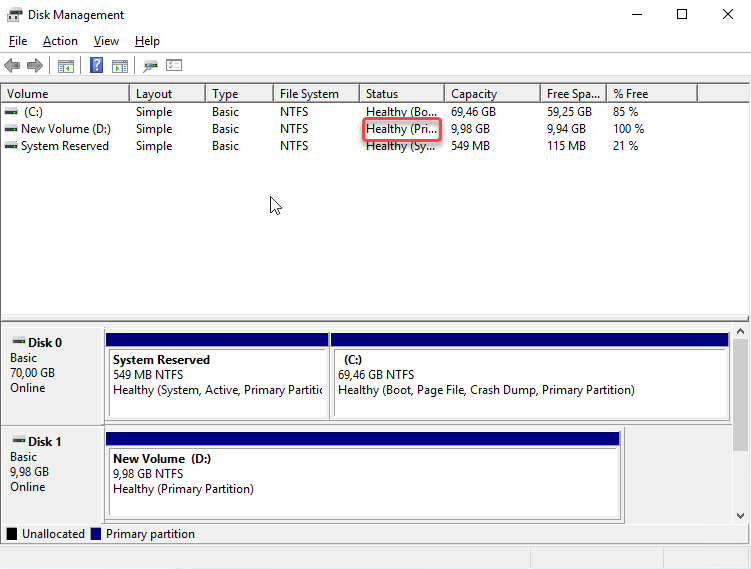
After you have completed the format wizard and volume, check the Status column in the list of mounted disks to make sure that the new disk has a Healthy. Now the disk is ready to use.
Last updated
